Cell ≫ 세포골격 ≫ ECM ≫ 바이오폴리머
세포 - ECM Extracellular matrix, Cell junction
세포골격, ECM
- 증점(단순)다당류 , 복합다당류
- 세포는 Fiber 덩어리다 , 세포는 콜라겐 덩어리다
- 콜라겐 Collagen , 콜라겐 조성 및 합성과정
- 엘라스틴 elastin, Proteoglycan
- Fibronectin, Laminins
- Integrins, Cadherins
- 담쟁이덩굴 : 아라비노갈락탄
- 세균(진핵,원핵), 고세균의 막구조
- glycobiology
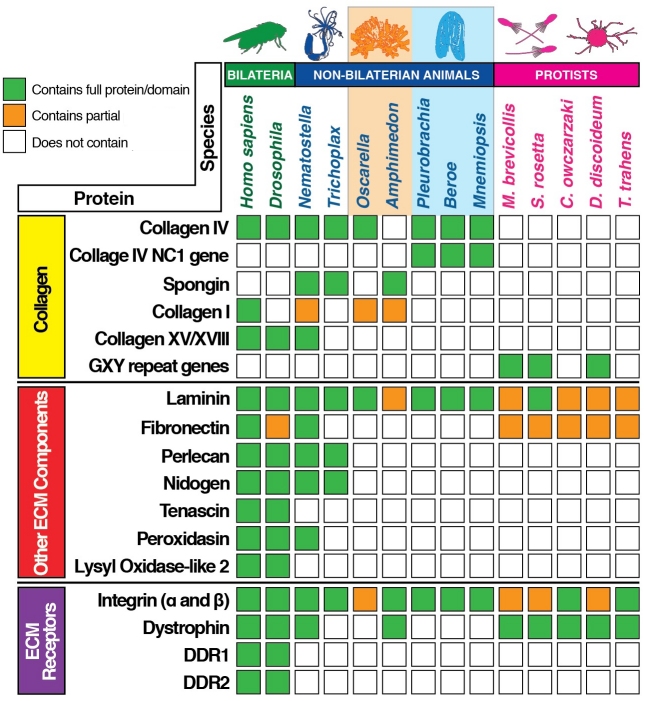
I. Extracellular Matrix (ECM) of Animal Cells nc1a, nc1b
A. variety of forms : nc2a, nc2b
- bone, cartilege, connective tissue
B. function of ECM nc4a, nc4b
1. helps determine cell shape
2. helps determine mechanical properties of cell
3. helps determine tissue properties
4. helps in cell recognition
5. helps in cell adhesion
C. three classes of molecules form ECM
1. structural proteins : give ECM strength(collagens) and flexibility(elastins)
2. protein-polysaccharide complexes
proteoglycans = provide matrix in which the other proteins are organized
3. adhesive glycoproteins : fibronectin, laminins
D. collagens are structural proteins of ECM
E. Elastins are structural proteins of ECM
F. Proteoglycan Matrix of ECM
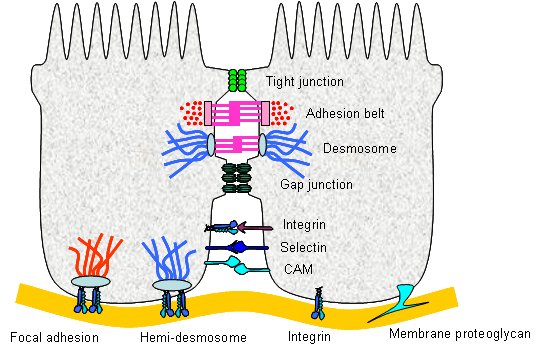
II. Adhesion and Cell-Cell Recognition
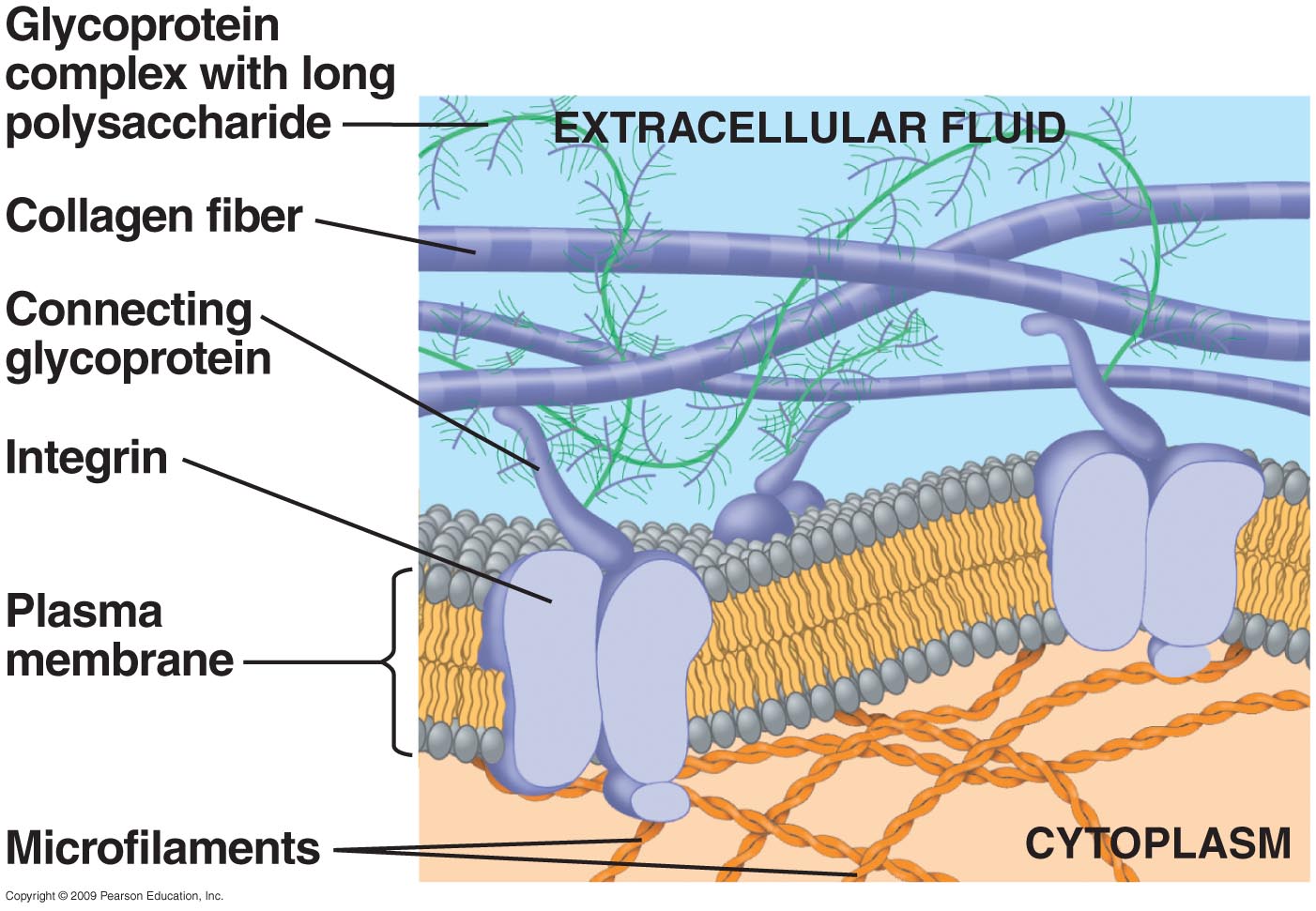
A. proteoglycans and the plasma membrane
1. adhesive glycoproteins found associated with PM
2. adhesive glycoproteins connect PM to ECM
3. two major types of adhesive glycoproteins
a. fibronectins, b. laminins
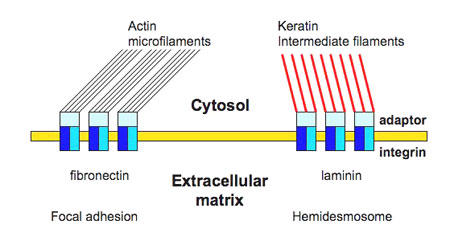
B. Fibronectin
C. Laminins
D. Integrins
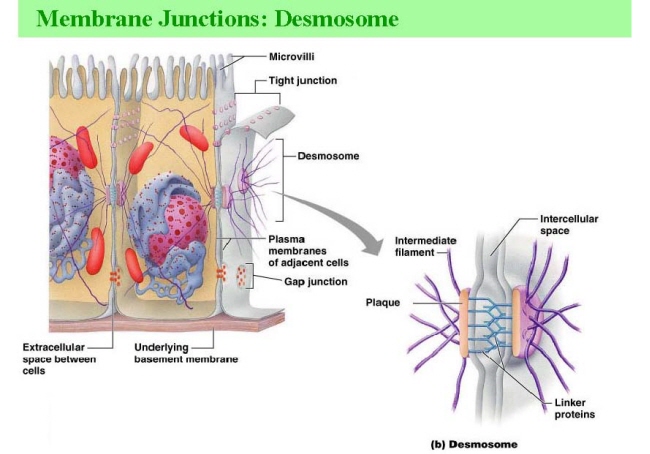
E. What holds cells together?
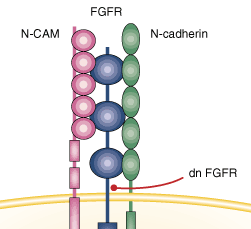
1) adhesive glycoproteins : cadherins, N-CAMs